|
|
před 10 roky | |
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| Images | před 10 roky | |
| readme.md | před 10 roky | |
| readme_vs.md | před 10 roky | |
readme.md
Hello, Android Quickstart
In this walkthrough, we create an application that translates an alphanumeric phone number entered by the user into a numeric phone number, and then calls that number. The final application looks like this:
Let's get started!
Requirements
Xamarin.Android works with any of the following setups:
- Latest version of Xamarin Studio on OS X Mountain Lion and above.
- Latest version of Xamarin Studio on Windows 7 and above.
- Windows 7 and above with Visual Studio 2010 Professional or higher.
This walkthrough assumes that the latest version of Xamarin.Android is installed and running on your platform of choice. For a guide to installing Xamarin.Android, refer to the Xamarin.Android Installation guides. Before we get started, please download and unzip the Xamarin App Icons & Launch Screens set.
Configuring Emulators
Android has several options for emulators. The standard Android emulator is the simplest to set up but runs slowly. Xamarin recommends that you use the high-performance Xamarin Android Player. If you are not using the Xamarin Android Player, you should configure your emulator to use hardware acceleration. Instructions for configuring hardware acceleration are available in the Accelerating Android Emulators guide.
Walkthrough
-
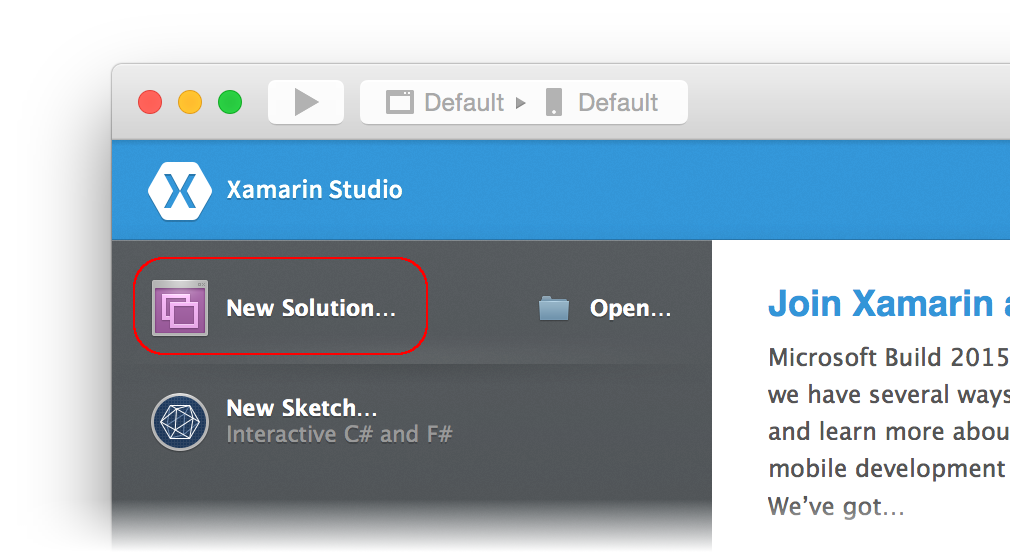
Let's launch Xamarin Studio from the Applications folder or from Spotlight. This opens the start page:
-
Click New Solution... to create a new project:
-
In the Choose a template for your new project dialog, let's click Android > App and select the Android App template. Click Next.
-
In the Configure your Android app dialog, we'll name the new app
Phonewordand click Next: -
In the Configure your new project dialog, we'll leave the Solution and Project names set to
Phonewordand click Create to create the project: -
After the new project is created, let‘s expand the Resources folder and then the layout folder in the Solution pad. Double-click Main.axml to open it in the Android Designer. This is the layout file for our screen:
-
Let‘s select the Hello World, Click Me! Button on the design surface and press the Delete key to remove it. From the Toolbox (the area on the right), enter
textinto the search field and drag a Text (Large) widget onto the design surface (the area in the center): -
With the Text (Large) widget selected on the design surface, we can use the Properties pad to change the
Textproperty of the Text (Large) widget toEnter a Phoneword:as seen below:Note: You can bring up the Properties pad or Toolbox at any time by navigating to View > Pads.
-
Next, let‘s drag a Plain Text widget from the Toolbox to the design surface and place it underneath the Text (Large) widget. Notice that we can use the search field to help locate widgets by name:
-
With the Plain Text widget selected on the design surface, we can use the Properties pad to change the
Idproperty of the Plain Text widget to@+id/PhoneNumberTextand change theTextproperty to1-855-XAMARIN: -
Let‘s drag a Button from the Toolbox to the design surface and place it underneath the Plain Text widget:
-
With the Button selected on the design surface, we can use the Properties pad to change the
Idproperty of the Button to@+id/TranslateButtonand change theTextproperty toTranslate: -
Next, let‘s drag a second Button from the Toolbox to the design surface and place it underneath the Translate button:
-
With the Button selected on the design surface, we can use the Properties pad to change the
Idproperty of the Button to@+id/CallButtonand change theTextproperty toCall:Let's save our work by pressing ⌘ + S.
-
Now, let‘s add some code to translate phone numbers from alphanumeric to numeric. We‘ll add a new file to the project by clicking on the gear icon next to the Phoneword project in the Solution pad and choosing Add > New File...:
-
In the New File dialog, let‘s select General > Empty Class, name the new file PhoneTranslator, and click New:
-
This creates a new empty C# class for us. Let‘s remove all of the template code and replace it with the following code:
using System.Text; using System; namespace Core { public static class PhonewordTranslator { public static string ToNumber(string raw) { if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(raw)) return ""; else raw = raw.ToUpperInvariant(); var newNumber = new StringBuilder(); foreach (var c in raw) { if (" -0123456789".Contains(c)) newNumber.Append(c); else { var result = TranslateToNumber(c); if (result != null) newNumber.Append(result); } // otherwise we've skipped a non-numeric char } return newNumber.ToString(); } static bool Contains (this string keyString, char c) { return keyString.IndexOf(c) >= 0; } static int? TranslateToNumber(char c) { if ("ABC".Contains(c)) return 2; else if ("DEF".Contains(c)) return 3; else if ("GHI".Contains(c)) return 4; else if ("JKL".Contains(c)) return 5; else if ("MNO".Contains(c)) return 6; else if ("PQRS".Contains(c)) return 7; else if ("TUV".Contains(c)) return 8; else if ("WXYZ".Contains(c)) return 9; return null; } } }Let's save the changes to the PhoneTranslator.cs file by choosing File > Save (or by pressing ⌘ + S), then close the file.
-
Next we‘re going to add code to wire up the user interface. Let‘s add the backing code into the
MainActivityclass. Double-click MainActivity.cs in the Solution Pad to open it: -
We begin by wiring up the Translate button. In the
MainActivityclass, find theOnCreatemethod. We'll add our button code insideOnCreate, below thebase.OnCreate(bundle)andSetContentView (Resource.Layout.Main)calls. Remove the template code so that theOnCreatemethod resembles the following code:using System; using Android.App; using Android.Content; using Android.Runtime; using Android.Views; using Android.Widget; using Android.OS; namespace Phoneword { [Activity (Label = "Phoneword", MainLauncher = true)] public class MainActivity : Activity { protected override void OnCreate (Bundle bundle) { base.OnCreate (bundle); // Set our view from the "main" layout resource SetContentView (Resource.Layout.Main); // Our code will go here } } } -
Next, we need to get a reference to the controls that we created in the layout file with the Android Designer. Let's add the following code inside the
OnCreatemethod:// Get our UI controls from the loaded layout: EditText phoneNumberText = FindViewById<EditText>(Resource.Id.PhoneNumberText); Button translateButton = FindViewById<Button>(Resource.Id.TranslateButton); Button callButton = FindViewById<Button>(Resource.Id.CallButton); -
Now let's add code that responds to user presses of the Translate button. Add the following code below the control definitions inside the
OnCreatemethod:// Disable the "Call" button callButton.Enabled = false; // Add code to translate number string translatedNumber = string.Empty; translateButton.Click += (object sender, EventArgs e) => { // Translate user’s alphanumeric phone number to numeric translatedNumber = Core.PhonewordTranslator.ToNumber(phoneNumberText.Text); if (String.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(translatedNumber)) { callButton.Text = "Call"; callButton.Enabled = false; } else { callButton.Text = "Call " + translatedNumber; callButton.Enabled = true; } }; -
Next let‘s add code that responds to user presses of the Call button. We‘ll place the following code below the code for the Translate button:
callButton.Click += (object sender, EventArgs e) => { // On "Call" button click, try to dial phone number. var callDialog = new AlertDialog.Builder(this); callDialog.SetMessage("Call " + translatedNumber + "?"); callDialog.SetNeutralButton("Call", delegate { // Create intent to dial phone var callIntent = new Intent(Intent.ActionCall); callIntent.SetData(Android.Net.Uri.Parse("tel:" + translatedNumber)); StartActivity(callIntent); }); callDialog.SetNegativeButton("Cancel", delegate { }); // Show the alert dialog to the user and wait for response. callDialog.Show(); }; -
Finally, let‘s give our application permission to place a phone call. Open the project options by right-clicking Phoneword in the Solution pad and selecting Options:
In the Project Options dialog, select Build > Android Application. In the Required Permissions section, enable the CallPhone permission:
-
Let's save our work and build the application by selecting Build > Build All (or by pressing ⌘ + B). If our application compiles, we will get a success message at the top of Xamarin Studio:
If there are errors, we can go through the previous steps and correct any mistakes until the application builds successfully.
-
We now have a working application – it‘s time to add the finishing touches! Let‘s start by editing the
Labelfor ourMainActivity. TheLabelis what Android displays at the top of the screen to let users know where they are in the application. At the top of theMainActivityclass, change theLabeltoPhone Wordas seen here:namespace Phoneword { [Activity (Label = "Phone Word", MainLauncher = true)] public class MainActivity : Activity { ... } } -
Next, let's set the application icon. First, let's open the downloaded and unzipped Xamarin App Icons set. Next, let's expand the drawable-hdpi folder under Resources and remove the existing Icon.png by right-clicking it and selecting Remove:
When the following dialog box is displayed, select Delete:
-
Next, let's right-click the drawable-hdpi folder and select Add > Add Files:
-
From the selection dialog, let's navigate to the unzipped Xamarin App Icons directory and open the drawable-hdpi folder. Select Icon.png:
-
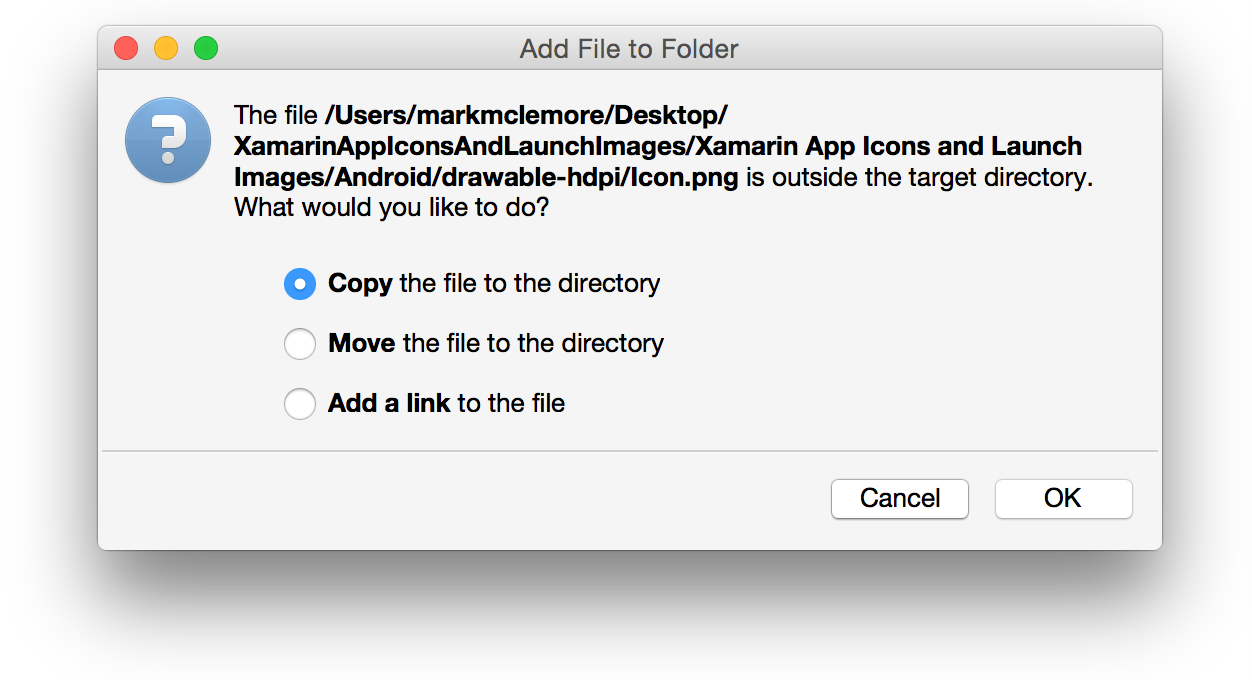
In the Add File to Folder dialog box, select Copy the file into the directory and click OK:
-
Repeat these steps for each of the drawable-* folders until the contents of the drawable-* Xamarin App Icons folders are copied to their counterpart drawable-* folders in the Phoneword project:
These folders provide different resolutions of the icon so that it renders correctly on different devices with different screen densities.
-
Finally, we can test our application by deploying it to an Android emulator. If you have not yet configured your emulator, please see Xamarin Android Player for setup instructions. In this example, we have installed the Nexus 4 (KitKat) (Android 4.4.2, API Level 19) virtual device and we have started it from the Xamarin Android Player Device Manager console:
In Xamarin Studio, select this virtual device (under Virtual Devices) and click the play button in the upper left corner:
As shown in this screenshot, we have selected the Nexus 4 (KitKat) (API 19) virtual device that is running in the Xamarin Android Player.
-
After Xamarin Studio loads the application into the virtual device, the Phoneword app is automatically started. The screenshots below illustrate the Phoneword application running in the Xamarin Android Player. The icons that we installed are displayed next to the Phone Word label that we configured in
MainActivity. Clicking the Translate button updates the text of the Call button, and clicking the Call button causes the call dialog to appear as shown on the right:
Congratulations on completing your first Xamarin.Android application! Now it's time to dissect the tools and skills we just learned in the Hello, Android Deep Dive.